|
Category - Skin tone and texture Back to the Decoder |
|
[Bl a] + [Bl b] + [Bl c] |
Acts on the skin’s natural pigmentation mechanisms to safely lighten skin.
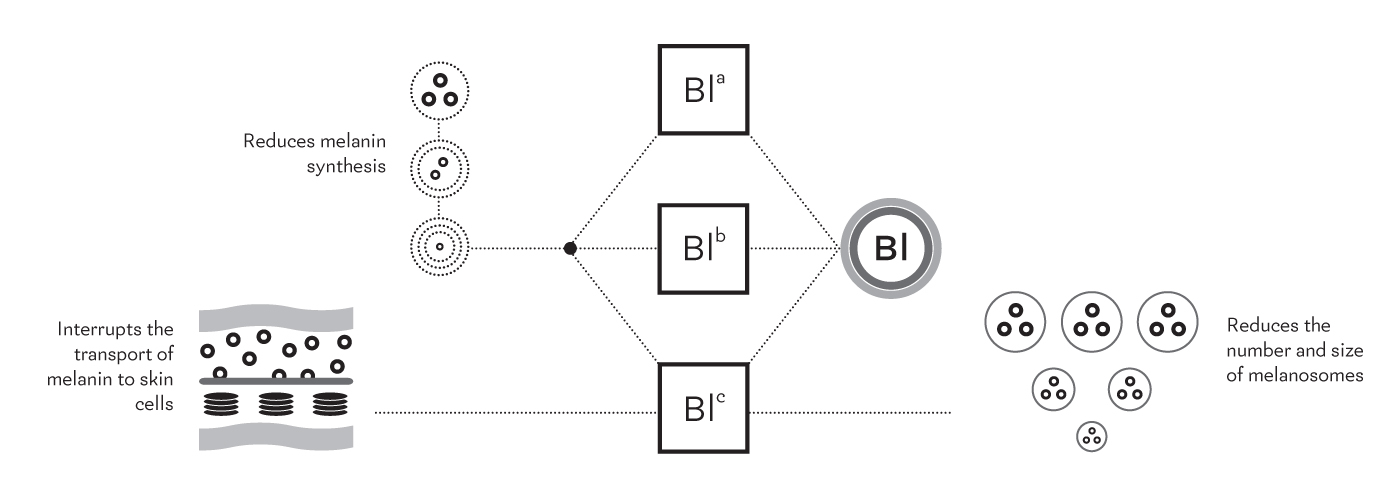
Lightening the skin is a societal phenomenon and standard of beauty for certain people, whether for cultural or social reasons. Yet most whitening products are dangerous. In fact, they often contain cortisone or corticoids that modify melanin and can cause various problems in the long term (hormonal issues, scarring, burns, etc.). Luckily, some products block the natural pigmentation process without causing harm. In fact, this process is quite easy to understand. First, under the effect of UV rays, the skin releases a hormone, which induces the melanocytes to synthesise melanin in the melanosomes. Melanin is responsible for skin pigmentation and melanosomes are vesicles for the storage and transport of melanin. Melanosomes are subsequently transferred to the epidermis, where they are broken down and eliminated. The melanin released in the process is destroyed more or less swiftly depending on each person’s background. Reducing the number and size of melanosomes is one way to interfere with the natural pigmentation process. Next, melanin synthesis can be reduced. Finally, the transport of melanin to the keratinocytes can be prevented. |
 |
||
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
|
Actives properties : |
||
|
|
[Bl a] |
[Bl b] |
[Bl c] |
Origins :Biomimetic peptide derived from the growth factor (TGF)-ß. |
Origins :A synergetic plant complex composed of a pea extract and a fatty acid attached to a sugar, sucrose dilaurate. |
Origins :Extract of brown algae, Dictyopteris membranacea, more commonly known as sea fern. |
Efficiency
|
Efficiency :
|
Efficiency :
|




